Spring Boot HateOAS Implementation
Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS) is a constraint of the REST application architecture that distinguishes it from other network application architectures. With HATEOAS, a client interacts with a network application whose application servers provide information dynamically through hypermedia.
The full project is on GitHub and can be accessed through the following link
This project will cover the following topics
- Initializing Spring Boot project using spring boot initializer.
- Date base connectivity using Hikari Data source.
- Creating Database Entities , Repositories & services using Spring JPA.
- Exposing an API using Spring web.
- Implementing HateOAS standard using Spring HateOAS.
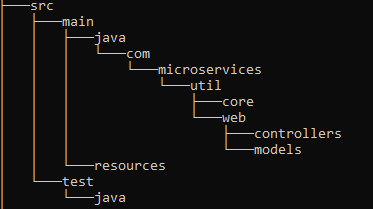
Project Architecture
Initializing Spring Boot project using spring boot initializer
Create your project using the spring Spring Initializr or if its imbedded in your IDE like Intellij you can start from there
Finish Creating your project and make sure you add the following dependencies
-
spring-boot-starter-hateoas
-
spring-boot-starter-web
-
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
-
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
-
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
-
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle.database.jdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc8</artifactId>
<version>21.1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
Date base connectivity using Hikari Data source.
Hikari is a JDBC DataSource implementation that provides a connection pooling mechanism. Compared to other implementations, it promises to be lightweight and better performing.
Start by creating a new package to organize and keep everything neat and tidy , for this tourtial I used oracle database.
Create a new class lets name it "oracleDataSource" the following is its implementation.
@Configuration
public class oracleDataSource {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource")
public HikariDataSource hikariDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder
.create()
.type(HikariDataSource.class)
.build();
}
}
Hikari Data source uses a configuration file which is in "Yaml" structure , so go ahead
and create that under resources "application.yaml".
define your connectivity inside as follows
app:
datasource:
jdbc-url: jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe
username: ****
password: ****
pool-size: 30
notice the line of configuration class corresponds to the path in the yaml configuration file
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource")
now that connectivity is done we can move to creating entities and exposing some methods using jpa.
Creating Database entities using Spring JPA
We are going to create the following entities described by the below UML in our database
create a new package "core" this is where all your database activity is kept , now create another package within core and lets call it "entities" and add the following classes implementation.
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.sql.Date;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_members")
public class membersEntity {
@javax.persistence.Id
@Column(name = "Id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
private Long Id;
@Column(name = "firstName")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "lastName")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
@Column(name = "telephoneNumber")
private String telephoneNumber;
@Column(name = "creationDate")
private Date creationDate;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "Id", referencedColumnName = "Id")
private memberDetailsEntity memberDetails;
public Long getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getTelephoneNumber() {
return telephoneNumber;
}
public void setTelephoneNumber(String telephoneNumber) {
this.telephoneNumber = telephoneNumber;
}
public Date getCreationDate() {
return creationDate;
}
public void setCreationDate(Date creationDate) {
this.creationDate = creationDate;
}
public memberDetailsEntity getMemberDetails() {
return memberDetails;
}
public void setMemberDetails(memberDetailsEntity memberDetails) {
this.memberDetails = memberDetails;
}
}
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_member_details")
public class memberDetailsEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "Id")
private Long Id;
private String country;
private String provinance;
private String streetName;
private String streetNumber;
private String buissnessDescription;
public Long getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getProvinance() {
return provinance;
}
public void setProvinance(String provinance) {
this.provinance = provinance;
}
public String getStreetName() {
return streetName;
}
public void setStreetName(String streetName) {
this.streetName = streetName;
}
public String getStreetNumber() {
return streetNumber;
}
public void setStreetNumber(String streetNumber) {
this.streetNumber = streetNumber;
}
public String getBuissnessDescription() {
return buissnessDescription;
}
public void setBuissnessDescription(String buissnessDescription) {
this.buissnessDescription = buissnessDescription;
}
@OneToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "Id")
private membersEntity member;
}
Now you need to create the repositories as extensions of crud repository , create a new package under core "repository".
import com.toutrial.resthateos.core.entities.membersEntity;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import java.util.Set;
public interface membersRepository extends CrudRepository<membersEntity,Long> {
Set<membersEntity> findAllByFirstNameOrLastName(String firstName,String lastName);
membersEntity findById(long Id);
}
import com.toutrial.resthateos.core.entities.memberDetailsEntity;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface memberDetailsRepository extends CrudRepository<memberDetailsEntity,Long>{
}
now for the services , create a new service class package under core "services".
the service acts as a business layer to access the queries.
@Service
public class membersBl {
@Autowired
private membersRepository members;
@Autowired
private memberDetailsRepository memberDetails;
public membersEntity createMember(membersEntity member){
try{
member.setCreationDate(new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
return members.save(member);
}catch (Exception ex) {
return null;
}
}
public Set<membersEntity> getAllByName(String name){
return members.findAllByFirstNameOrLastName(name,name);
}
public membersEntity getById(long Id){
return members.findById(Id);
}
public Optional<memberDetailsEntity> getDetailsById(long Id){
return memberDetails.findById(Id);
}
}
Exposing an API using Spring web.
What you need to build a rest service is a controller and model , lets start by building the model used by the service.
the model here is basically what the API consumes and produces
create a package lets call it web , create another package under that and name it models.
Member Model
notice that the model created extends RepresentationModel<> which is a container for a collection
of Links and provides APIs to add those links to the existing model.
public class memberModel extends RepresentationModel<memberModel> {
private Long Id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String telephoneNumber;
private String email;
private Date creationDate;
public Long getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getTelephoneNumber() {
return telephoneNumber;
}
public void setTelephoneNumber(String telephoneNumber) {
this.telephoneNumber = telephoneNumber;
}
public Date getCreationDate() {
return creationDate;
}
public void setCreationDate(Date creationDate) {
this.creationDate = creationDate;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
Member Details Model
public class memberDetailsModel extends RepresentationModel<memberDetailsModel> {
private Long Id;
private String country;
private String provinance;
private String streetName;
private String streetNumber;
private String buissnessDescription;
public Long getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getProvinance() {
return provinance;
}
public void setProvinance(String provinance) {
this.provinance = provinance;
}
public String getStreetName() {
return streetName;
}
public void setStreetName(String streetName) {
this.streetName = streetName;
}
public String getStreetNumber() {
return streetNumber;
}
public void setStreetNumber(String streetNumber) {
this.streetNumber = streetNumber;
}
public String getBuissnessDescription() {
return buissnessDescription;
}
public void setBuissnessDescription(String buissnessDescription) {
this.buissnessDescription = buissnessDescription;
}
}
in a normal rest api you can associate the member model to the member details model but since we
are implementing hateos we are using links to retrieve the data at need
now lets create the controller , create a member controller class under the package controllers
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/member/")
public class memberController {
@Autowired
membersBl membersService;
@GetMapping(path = "getByName/{name}")
public CollectionModel<memberModel> getMemberByName(@PathVariable("name") String name){
List<memberModel> members = new ArrayList<>();
membersService.getAllByName(name).stream().forEach(membersEntity -> {
memberModel member = new memberModel();
member.setId(membersEntity.getId());
member.setCreationDate(membersEntity.getCreationDate());
member.setFirstName(membersEntity.getFirstName());
member.setLastName(membersEntity.getLastName());
member.setEmail(membersEntity.getEmail());
member.setTelephoneNumber(membersEntity.getTelephoneNumber());
//Link selfLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)).slash(name).withSelfRel();
//member.add(selfLink);
Link memberLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)
.getById(member.getId())).withRel("getById");
member.add(memberLink);
Link memberDetailsLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)
.getDetailsById(member.getId())).withRel("getDetailsById");
member.add(memberDetailsLink);
members.add(member);
});
Link link = linkTo(memberController.class).slash("getByName").slash(name).withSelfRel();
CollectionModel<memberModel> result = CollectionModel.of(members, link);
return result;
}
@GetMapping(path = "getById/{Id}")
public memberModel getById(@PathVariable("Id") long Id){
membersEntity membersEntity = membersService.getById(Id);
memberModel member = new memberModel();
member.setId(membersEntity.getId());
member.setFirstName(membersEntity.getFirstName());
member.setLastName(membersEntity.getLastName());
member.setEmail(membersEntity.getEmail());
member.setTelephoneNumber(membersEntity.getTelephoneNumber());
member.setCreationDate(membersEntity.getCreationDate());
Link link = linkTo(memberController.class).slash("getById").slash(Id).withSelfRel();
member.add(link);
return member;
}
@PostMapping(path = "createMember")
public actionModel createMember(@RequestBody memberModel member){
membersEntity memberRecord = new membersEntity();
memberRecord.setFirstName( member.getFirstName());
memberRecord.setLastName(member.getLastName());
memberRecord.setEmail(member.getEmail());
memberRecord.setTelephoneNumber(member.getTelephoneNumber());
memberRecord = membersService.createMember(memberRecord);
actionModel result = new actionModel();
if(memberRecord.getId() > 0){
result.setAction(true);
result.setMessage("success");
Link memberLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)
.getById(memberRecord.getId())).withRel("getById");
result.add(memberLink);
}else{
result.setAction(false);
result.setMessage("failed");
}
return result;
}
@PostMapping(path = "getDetailsById/{Id}")
public memberDetailsModel getDetailsById(long Id){
Optional<memberDetailsEntity> mDetails = membersService.getDetailsById(Id);
memberDetailsModel model = new memberDetailsModel();
mDetails.ifPresent(memberDetailsEntity -> {
model.setId(memberDetailsEntity.getId());
model.setCountry(memberDetailsEntity.getCountry());
model.setProvinance(memberDetailsEntity.getProvinance());
model.setStreetName(memberDetailsEntity.getStreetName());
model.setStreetNumber(memberDetailsEntity.getStreetNumber());
model.setBuissnessDescription(memberDetailsEntity.getBuissnessDescription());
Link link = linkTo(memberController.class).slash("getDetailsById").slash(Id).withSelfRel();
model.add(link);
});
return model;
}
}
This Code Snippet utilizes the extended model to reference the service links used to retrieve detail data
now you can populate your data base and run the application , using a client invoke the method
Link memberLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)
.getById(member.getId())).withRel("getById");
member.add(memberLink);
Link memberDetailsLink = linkTo(methodOn(memberController.class)
.getDetailsById(member.getId())).withRel("getDetailsById");
member.add(memberDetailsLink);
Link link = linkTo(memberController.class).slash("getByName").slash(name).withSelfRel();
CollectionModel<memberModel> result = CollectionModel.of(members, link);
"getByName" => /api/v1/member/getByName/yacoub
notice the model is returned in a _embeded tag and the links added successfully to the service response