What are Microservices?
Microservices are an architectural and organizational approach to software development where software is composed of small independent services that communicate over well-defined APIs
Project Design
What you will need?
- Java 1.8 or later
- Maven
- Intellij IDE
- Any Type of SQL DB
Project Setup
- Install Maven Plugin using the following link
- Navigate to your directory that you need where the project is created and run the below command
- Open the created project in IntelliJ IDE.
- Select the module type as maven.
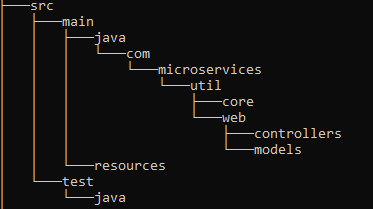
- Click finish you should find the project structure below.
- Open the customer pom file, and notice the parent reference.
- Now notice the parent pom file having the created module referenced.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>@SpringBootApplication annotation is used to mark a configuration class that declares one or more @Bean methods and also triggers auto-configuration and component scanning.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class CustomerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(CustomerApplication.class,args);
}
}2) Create the Entity Class
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity
@Table(name="customer")
public class CustomerEntity {
@javax.persistence.Id
@Column(name = "Id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long Id;
@Column(name = "firstName")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "lastName")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
}
import com.microservices.customer.core.entities.CustomerEntity;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface CustomerRepository extends CrudRepository<CustomerEntity,Long> {
}
4) Create the Customer Service Class.
@Service annotates classes at the service layer.
@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
public CustomerEntity registerCustomer(CustomerEntity customerEntity){
return customerRepository.save(customerEntity);
}
}
HikariDataSource
Hikari is the default DataSource implementation with Spring Boot 2
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class CustomerDS {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource")
public HikariDataSource hikariDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder
.create()
.type(HikariDataSource.class)
.build();
}
}
app.datasource.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://IP:Port/microservices_customer?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=UTF-8
app.datasource.username=
app.datasource.password=
app.datasource.pool-size=30# Hibernate
spring.datasource.initialize=true
#spring.datasource.platform=oracle
#update-validate-create-
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=create
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.implicit-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.ImplicitNamingStrategyLegacyJpaImpl
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
6) Moving on to the Rest Service , you will need to create a model and a controller
- Model Class
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class CustomerModel {
private long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
}
- Controller Class
import com.microservices.customer.core.entities.CustomerEntity;
import com.microservices.customer.core.services.CustomerService;
import com.microservices.customer.web.models.CustomerModel;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/v1/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
CustomerService customerService;
@PostMapping(path = "/registerCustomer")
public CustomerModel registerCustomer(@RequestBody CustomerModel customerModel) {
CustomerEntity customerEntity =
customerService.registerCustomer(new CustomerEntity(null,
customerModel.getFirstName(),
customerModel.getLastName(),
customerModel.getEmail()));
return new CustomerModel(customerEntity.getId(),
customerEntity.getFirstName(),
customerEntity.getLastName(),
customerEntity.getEmail());
}
}
Now let's test what we have build , run the customer application class and use postman or any other client to test the microservice.Record was created succefully in the database.
- Creating the Email Notification Microservice.
Create a new module based on maven and name it util , this will hold all our utility microservices.
Notice that the util module is refrenced in the main pom.xmlI will be using the following strucutre to organize my code1) Add the following dependancies in the util pom.xml file.<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2) Create the util application class under the main package "com.microservices.util".3) Create the Email Sender Intrerface to allow future dependancy Injection.import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class UtilApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(UtilApplication.class,args);
}
}public interface EmailSender {4) Create the Email Util Implementation Class.
boolean sendEmail(String to,String subject,String email);
}@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class EmailUtil implements EmailSender {
@Autowired
private final JavaMailSender mailSender;
@Override
@Async
public boolean sendEmail(String to,String subject,String email) {
try {
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,"utf-8");
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setText(email);
helper.setSubject(subject);
helper.setFrom("Hello@microservices.com");
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}catch (Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}5) Now lets create the controller and model
- Model Class
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class EmailModel {
private String to;
private String subject;
private String text;
}
- Controller Class
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "api/v1/email")
public class EmailController {
@Autowired
private EmailUtil emailUtil;
@PostMapping(path = "/send")
public boolean sendEmail(@RequestBody EmailModel emailModel){return emailUtil.sendEmail(emailModel.getTo(), emailModel.getSubject(),}
emailModel.getText());
}6) Finally add the configuration needed to send email in the application.properties filei will be using gmail.spring.application.name=Util
server.port=8083
spring.mail.host=smtp.gmail.com
spring.mail.port=587
spring.mail.username=
spring.mail.password=
# Other properties
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.auth=true
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.connectiontimeout=5000
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.timeout=5000
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.writetimeout=5000
# TLS , port 587
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.starttls.enable=trueFor the sake of testing you will need to enable less secure apps on gmail.Now Lets run the Util Application Class and test the microservice using a client.Acheving Http Communication between Microservices.
- Open the customer module and add the following referance to the email microservice to the application.properties file.
notification.service.url=http://IP:Port/api/v1/email/send
- Create the Configuration class Customer Config
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class CustomerConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
- Create the Outbound Reqeust Model Bean
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Builder
public class NotificationServiceRequest {
private String to;
private String subject;
private String text;}
- Modify the Customer Service Class to the following
Now lets test the changes@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Autowired
Environment environment;
@Autowired
RestTemplate restTemplate;
public CustomerEntity registerCustomer(CustomerEntity customerEntity){customerEntity = customerRepository.save(customerEntity);}
String emailBody = "New customer was registred with the user " +
customerEntity.getFirstName() + " " +customerEntity.getLastName();
NotificationServiceRequest notificationServiceRequest = new NotificationServiceRequest(
customerEntity.getEmail(),
"Registration Confirmation",
emailBody
);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<NotificationServiceRequest> httpEntity =
new HttpEntity<>(notificationServiceRequest, headers);
restTemplate.postForObject(
environment.getProperty("notification.service.url"),
httpEntity,
String.class
);
return customerEntity;
}
And the recived email upon registration.
Thats it , to be hounest this is the bare minimum , you can achieve so much more with the microservices architectural pattern.






















No comments:
Post a Comment